Bipartite networks
A bipartite network, also known as a bipartite graph or bigraph, is a type of network in graph theory where the nodes can be divided into two distinct sets, and there are only connections between nodes from different sets. In other words, there are no connections between nodes within the same set.
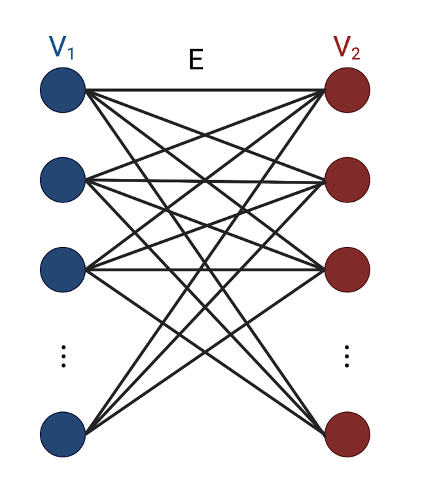
Formally, a bipartite network is defined as a graph G(V, E), where V is the set of nodes, and E is the set of edges. The node set V can be partitioned into two disjoint sets, V₁ and V₂, such that each edge in E connects a node from V₁ to a node from V₂. This property distinguishes bipartite networks from other types of networks where connections can occur between any pair of nodes.
Bipartite networks are commonly used to represent relationships or interactions between two distinct sets of entities. For example, in a social network, one set of nodes can represent individuals, while the other set represents groups or organisations. The edges in the bipartite network indicate connections between individuals and the groups they belong to.
Bipartite networks have various applications in different fields, such as recommendation systems, collaboration networks, ecological networks, and information retrieval. Analysing bipartite networks can help uncover patterns, understand relationships, and gain insights into the interactions between different sets of entities.